The name "Google" originated from a misspelling of the word "googol",which refers to 10100, the number represented by a 1 followed by one hundred zeros. Having found its way increasingly into everyday language, the verb "google" was added to the Merriam Webster Collegiate Dictionary and the Oxford English Dictionary in 2006, meaning "to use the Google search engine to obtain information on the Internet." Google began in January 1996, as a research project by Larry Page, who was soon joined bySergey Brin, when they were both PhD students at Stanford University in California. They hypothesized that a search engine that analyzed the relationships between websites would produce better ranking of results than existing techniques, which ranked results according to the number of times the search term appeared on a page. Their search engine was originally nicknamed "BackRub" because the system checked backlinks to estimate the importance of a site. A small search engine called Rankdex was already exploring a similar strategy. Google use the algorithm called page rank algorithm
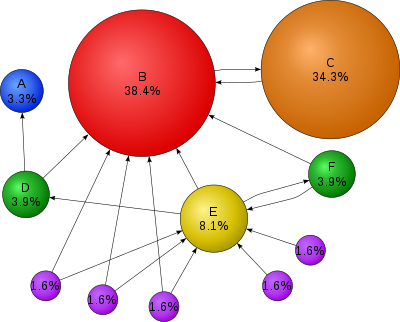
PageRank is a link analysis algorithm, named after Larry Page,[1] used by the GoogleInternet search engine that assigns a numerical weighting to each element of a hyperlinkedset of documents, such as the World Wide Web, with the purpose of "measuring" its relative importance within the set. The algorithm may be applied to any collection of entities with reciprocal quotations and references. The numerical weight that it assigns to any given element E is also called the PageRank of E and denoted by PR(E). In other words, a PageRank results from a "ballot" among all the other pages on the World Wide Web about how important a page is. A hyperlink to a page counts as a vote of support. The PageRank of a page is defined recursively and depends on the number and PageRank metric of all pages that link to it ("incoming links"). A page that is linked to by many pages with high PageRank receives a high rank itself. If there are no links to a web page there is no support for that page.
Google assigns a numeric weighting from 0-10 for each webpage on the Internet; this PageRank denotes a site’s importance in the eyes of Google. The PageRank is derived from a theoretical probability value on a logarithmic scale like the Richter Scale. The PageRank of a particular page is roughly based upon the quantity of inbound links as well as the PageRank of the pages providing the links. It is known that other factors, e.g. relevance of search words on the page and actual visits to the page reported by the Google toolbar also influence the PageRank.[citation needed] In order to prevent manipulation, spoofing and Spamdexing, Google provides no specific details about how other factors influence PageRank.[citation needed]
Numerous academic papers concerning PageRank have been published since Page and Brin's original paper.[5] In practice, the PageRank concept has proven to be vulnerable to manipulation, and extensive research has been devoted to identifying falsely inflated PageRank and ways to ignore links from documents with falsely inflated PageRank


No comments:
Post a Comment